고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문

- Download the latest versions of the best Mac apps at safe and trusted MacUpdate. The attributes can be used to detect when a hard drive is having mechanical or electrical. I would like to point out our own app SSD Health Check:.
- Here is the list of best Windows and Mac Free Tools to Check SSD Health and Monitor Performance. Crystal Disk Info You can use this tool to check your SSD and other Hard Disk types.
- Hard Disk Health Check Tool
- Hard Disk Health Check Software For Mac
- Hard Disk Health Checker For Mac Pro
Your hard drive is the soul of your PC, the place where all your most important data is stored. While most PC components can be replaced, the invaluable data on your hard drive can’t if you haven’t created a backup. For this reason, ensuring your hard drive stays healthy is crucial (anyone get the dull hard drive-related pun?).
There are various ways to check on your hard drive health – from built-in methods in Windows to your HDD manufacturer’s diagnostic tools, and we’re going to talk you through the best methods. Use The HDD Manufacturer’s Tools Most major hard drive manufacturers provide free robust tools to monitor your hard drive health and performance. The first step to knowing which one to use is, of course, knowing the make of your hard drive.
HDD Health is a good hard disk life checker for. Constant monitoring; SMART attributes info; predicting HDD failure; Checking SSD status. Remember that detecting a problem at earlier stages and backing up your data is better than losing and restoring it, which is more time-consuming and complicated.
If you know the make of your hard drive, you can skip this part. If you don’t, press the Win key, type “device manager” and click it when it appears in the search results. In Device Manager unstack the “Disk drives” option and make a note of the model number of your hard drive. Next, type the model number into Google to bring up results that will show you the make of the hard drive. After that, go to the manufacturer’s support page and search for their hard drive utility. To help you out, here are links to the relevant download pages of some of the biggest hard drive brands:. Each of these tools functions a little differently, but most importantly, each one has diagnostic features that let you test your hard drive health.
Windows CHKDSK Tool Windows CHKDSK Tool is a built-in Windows tool that will scan your disk to find system errors and bad sectors and show if there are any problems with your hard disk. It will both scan and fix problems it can fix and will let you know if there is a bigger problem that it can’t fix. You can use this tool to both check hard disk health and fix bad sectors and errors if possible.
To use CHKDSK, right-click on the drive which you would like to check for errors, and select “Properties.” Then click on the “Tools” tab, and then click on the “Check now” button. A dialog will open up with two options to fix errors and scan for bad sectors. You can select these options if you want to fix errors and bad sectors; otherwise you can just click on “Start” to get a basic report of hard disk problems (if there are any).
This tool is very basic and focuses on finding system errors and bad sectors. It will just let you know if there are any big problems and nothing more, so only use it as a basic hard disk checking and fixing tool. Use WMIC WMIC is a command-line interface that lets you perform many administrative tasks, including checking hard disk health. It uses the S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) feature of hard disks to see status and provide a simple conclusion, like “OK” or “Pred Fail,” etc. It is still a very basic command that offers very little information, but it is quick and a built-in feature of Windows. To check a hard disk with WMIC, press the Win + R buttons to open the Run dialog.
Type cmd and click “OK” to open the Windows command prompt. Diskdrive get status and press Enter again. You will see the status of your hard disk after a short delay. Use a Third-Party Hard Disk Health Checking Tool You can also use a third-party hard disk health checking tool that will offer much more information than just good or bad status. These tools use the same “S.M.A.R.T” feature of hard disks to fetch data, just like WMIC. However, they provide all the details to you, instead of just showing good or bad status.
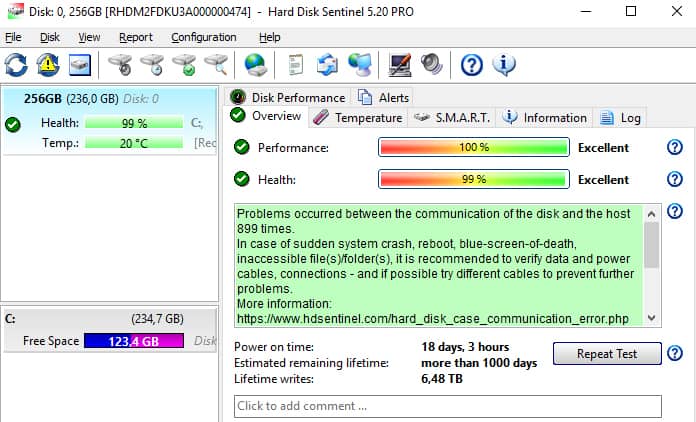
CrystalDiskInfo For this purpose, is a really simple, yet powerful, tool. It is a free-to-use tool that is extremely light and offers all the required information, such as temperature, health status, hard disk type and features, and other attributes like read/write error rate and spin-up time, etc. The standard tool comes as a 4 MB.exe file, and its installer contains ads, so make sure you use the “Custom Installer” option and uncheck the side tool (ad). Once installed, all you need to do is launch the program, and you will see all the information about your hard disk(s) in the main interface.
The tool will also check the hard disk health after every 10 minutes (by default) and alert you if there is anything wrong. There are also other third-party hard disk health-checking tools like. These are much more advanced with loads of extra features, but for an average user CrystalDiskInfo should work perfectly.
HDDScan is a freeware software for hard drive diagnostics (RAID arrays servers, Flash USB and SSD drives are also supported). The program can test storage device for errors (Bad-blocks and bad sectors), show S.M.A.R.T.
Attributes and change some HDD parameters such as AAM, APM, etc. HDDScan can be useful for performing the regular 'health test' for your drive and predicting its degradation, so you will be able to prevent data loss and backup your files before you would have to contact the data recovery service. HDDscan is a free – noncommercial utility designed to prevent and detect errors on majority of storage devices however it is not meant to fix or repair physically damaged data storage devices (ssd, hard drives, removable drives or mobile phones.
Hard Disk Health Check Tool
If your device is making any abnormal noises (Good resource of bad sounds can be found ). Stop immediately, do not try to turn on the device and contact a professional data recovery company – preferably with a Cleanroom or at least a clean bench. Is recommended and approved by the developers of the HDDScan utility. Additionally, software can be used as the hard disk temperature monitor and reading/writing benchmark – performance graph is displayed for every test.
Capabilities and Requirements: Supported storage devices:. IDE (ATA) and SATA HDD. SCSI (SAS) HDD. External USB drives and all major USB boxes (see Appendix A). FireWire or IEEE 1394 HDD (see Appendix A). RAID volumes made of ATA (IDE) / SATA / SCSI HDDs (surface tests only). USB Flash (pen drives) – surface tests only.
SATA / ATA SSD – solid state drives. Storage device tests:.
Verification in linear mode – helps to determine if your drive needs data rescue, has recoverable errors or in its perfect shape. Reading in linear mode – simpler, but faster disk check. Erasing in linear mode. Reading in Butterfly mode (synthetic random read).
Hard Disk Health Check Software For Mac
S.M.A.R.T.:. Reading and analyzing SMART parameters from ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire HDD.
Reading and analyzing Log Pages from SCSI HDD. SMART tests running on ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire HDD. Temperature monitor for ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire/SCSI HDD. Additional features:.
Reading and analyzing identity information from ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire/SCSI HDD. Changing AAM, APM, PM parameters on ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire HDD.
Reporting defect information on SCSI HDD. Spindle start/stop function on ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire/SCSI HDD.
Reports can be saved in MHT format. Reports can be printed.
Skins support. Command line support. SSD SMART and Identity reports. Requirements:. Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003 (with restrictions), Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 (NEW). The program shouldn’t be run from a read-only device/media. User interface Main view Main view.
Control elements:. Select Drive drop box - contains a list of supported storage devices in a system.
The list contains models and serial numbers of the devices. Icon defines possible storage type. Button – generates S.M.A.R.T. Attributes report.
TESTS button – shows pop-up menu to select read and write tests. TOOLS button – shows pop-up menu to select available drive’s controls and features. More button – shows drop-down menu with program controls. When you click on TEST button, the pop-up menu offers you one of the tests. If you select any test – the Test selection dialog will be opened. Test selection pop-up. Control elements:.
Hard Disk Health Checker For Mac Pro
FIRST SECTOR – determines first Logical Block Address (LBA) for testing. SIZE – a number of LBAs for this test. BLOCK SIZE– indicates Block Size for testing (in LBA sectors). Previous button – returns the program on the Main screen.
Next button – adds the test into a tasks’ queue. Tests capabilities and limitations:. Only one test at a time. Author wasn’t able to get stable test results with two or more simultaneous tests. Verify test may have restrictions on Block Size with 256, 16384 or 65536 sectors because of Windows limitations. Verify test may work in unreliable way on USB/Flash devices. In Verify mode device reads block of data into drive’s internal buffer only and checks for consistency, there is no data transfer through an interface connector/cable.
The program measures operation time for each block. The program tests blocks one by one from minimum to maximum. In Read mode device reads block of data and transfers it thorough interface to the host controller. The program reads block of data into a temporary buffer and measures time of operation for each block. The program tests blocks one by one from minimum to maximum. In Erase mode the program prepares block of data field with special pattern and an LBA number.
The program sends the block of data to the drive and the drive writes the block (All previous data in the block on the drive will be overwritten with the pattern and cannot be recovered after that!) The program measures operation time for each block. The program tests blocks one by one from minimum to maximum. Butterfly Read mode is similar to Read mode difference only in blocks’ order. Blocks are tested by pairs. The first block in the first pair will be Block 0, the second block in the first pair will be Block N (where N is number of last block for testing).
Next pair will be Block 1 and Block N-1. Test ends in the middle of the testing area. The program measures operation time. Tasks Manager window. This window shows a tasks queue. All surface tests, S.M.A.R.T.
Tests and Temperature Monitor tasks will be displayed in the Tasks Manager Window. Double clicking on a task line will open task information window (alternatively you can select Show Details option from the menu of the Tasks Manager). Test information window This window contains information about selected test.
Test could be paused or stopped and report with results can be generated. Graph Tab: Displays testing speed for each block. Information is represented as a graph.
Tests The program can run three types of tests. Short test – lasts about 1-2 minutes. The test inspects drive’s main electronics, scans small part of drive’s surface and checks sectors from the Pending-list (such sectors may have read errors). This test recommended for a quick drive testing. Extended test – could take 0.5-60 hours, depending of the size of the drive. The test inspects drive’s main electronics and scans the whole drive’s surface.
Conveyance test – usually lasts several minutes. The test inspects drive’s main electronics and logs that may have records which could indicate incorrect transportation or storing. The SMART Test can be selected from the SMART tests dialog that can be called by pressing SMART TESTS button SMART Tests Dialog. Features The program might be able change some parameters for ATA/SATA/USB/FireWire HDD:. AAM – this function changes drive’s acoustic. If this function enabled drive’s noise may be decreased by smoothing HSA’s seek operations.
HDD could lose some performance. APM – this function allows power savings by temporary decreasing spindle’s rotation speed (including complete stop) when drive is in idle. PM – this function allows setting spin-down timer. If drive is in idle spindle would be stopped after the time set in the timer. If any program requests HDD access the internal timer will be reset and spindle will continue to spin.
The program can also start or stop spindle immediately. If any program requests HDD access drive’s spindle will spin up. Features window for ATA/SATA HDD.





